Space
Our vision
By 2025, Queensland’s space industry will be recognised as a leading centre in Australasia for launch activities, ground systems, Earth observation, niche manufacturing, robotics and automation for space.
We're committed to growing the state’s space industry.
Quick links
Queensland Space Industry Strategy
The Queensland Government is working to transform the state’s economy and create high-paid, knowledge-based jobs for our future, particularly in regional Queensland. A key part of this work is recognising and supporting the jobs and industries of the future, such as those from the $370 billion global space economy.
The government’s objectives and activities to grow the Queensland space industry are set out in the Queensland Space Industry Strategy 2020 – 2025 (![]() 2.5 MB).
2.5 MB).
Strategies and priority actions
We will deliver this vision through two key strategies.
- Sustain and strengthen Queensland’s space industry capability
- Expand Queensland’s space industry by connecting with the growing domestic and international space markets
Queensland’s opportunity in space
-
World class supporting industries and R&D.
-
Advantageous location for launch
-
The space industry could contribute between $3.5 - $6 billion to our economy by 2036.
Australia’s space industry generates around $3-4 billion in revenue a year and employs some 10,000 people. The Australian Space Agency has an ambitious but achievable goal to triple the size of Australia’s space economy and create up to 20,000 additional jobs by 2030.
Queensland is well positioned to lead Australia in this emerging industry. Our expanding space economy already supports over 2200 jobs and generates more than $810 million in direct annual revenue.
Queensland already has 20% of the nation’s estimated space-related jobs and also has industrial and geographical advantages that make it uniquely positioned to support global space activities and bolster Australia’s sovereign space capability.
Queensland’s space industry could directly create up to 6000 high-value Queensland jobs and contribute between $3.5 and $6 billion to the state economy by 2036. Many of these new jobs could be clustered in regional Queensland through the development of space infrastructure. This will create new business opportunities and an industry supply chain to service them.
The space economy already adds $520 million in value to the Gross State Product. The full potential of space-enabled services has not yet been realised in Australia. Increasing the uptake of space-related goods and services through Queensland’s industries such as agriculture and mining could contribute $1.1-1.7 billion in productivity by 2036.
Key growth areas for Queensland’s space economy
-
Leveraging Queensland’s industry and geographical strengths to grow the space industry.
-
Connecting Queensland organisations to the growing global space economy and to industries that can benefit from space-related services.
-
Strengthening Queensland’s existing space capability to be world-class and competitive.
Queensland’s strengths
-
The annual global launch services market is worth US$5.7 billion and growing. Reducing launch costs, combined with the rising demand for space-enabled services, are driving the demand for rocket launches and creating opportunities to launch, operate, manufacture, test and develop launch supply chains.
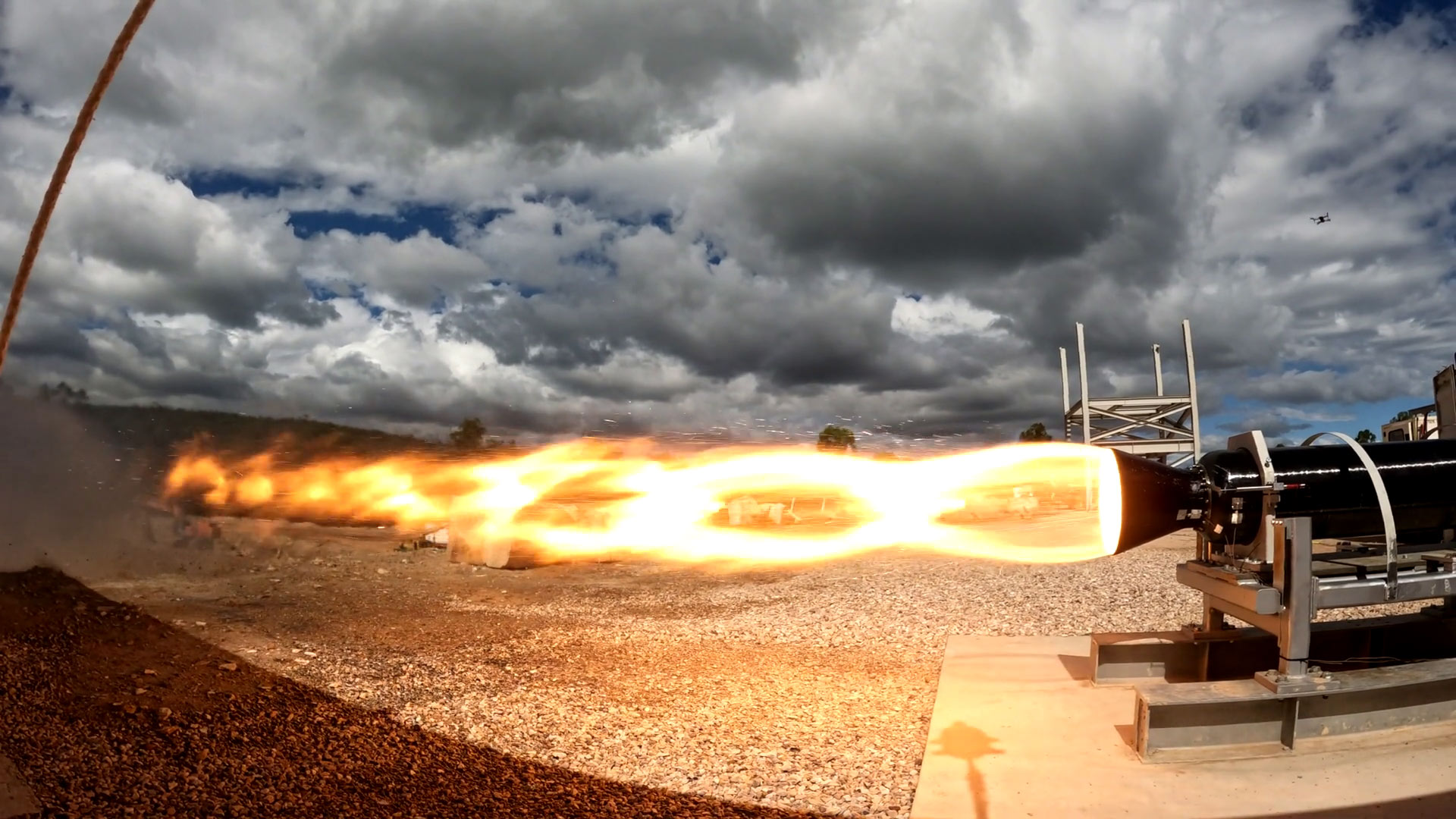 Image courtesy of Rocket Technologies International
Image courtesy of Rocket Technologies InternationalIn Queensland, Black Sky Aerospace, Gilmour Space and Hypersonix are developing affordable access to space for small- and medium-sized payloads.
Launching from Queensland
There are a number of technical considerations to identifying a suitable launch location.
Queensland is the only state on Australia’s eastern seaboard with direct access to equatorial orbits. Ideal latitude, clear skies and open waters to the east means that Queensland can launch larger payloads, and into more orbits, than any other place in Australia.
Queensland’s coastline is comparable and at better latitudes to Cape Canaveral, Florida, which hosts the Kennedy Space Centre; one of the world’s busiest launch sites.
Opportunity for launch
Queensland’s geographical attributes, skilled workforce and innovative industry position the state to expand its place in the world’s growing launch supply chain.
Some opportunities to support the development of Queensland’s launch industry include:
- National support and leadership – launch is a national capability that supports the growth in Australia’s space industry and sovereign capability. A national approach to capability development is key to optimising these benefits.
- Support for enabling infrastructure – development of enabling infrastructure to test launch vehicles, components and payloads will strengthen Queensland and Australia’s launch supply chain. Key considerations are a static test site and an orbital launch facility in proximity to launch vehicle developers.
- A versatile launch site – that can launch to multiple orbits and cater for multiple users. A Queensland launch facility would bolster national capability, providing the Southern Hemisphere with a launch location accessible to international markets.
-
A prime location
Ground stations, often situated in satellite parks, track and control satellites and download data, including in real time to customer industries for time-based analytics.
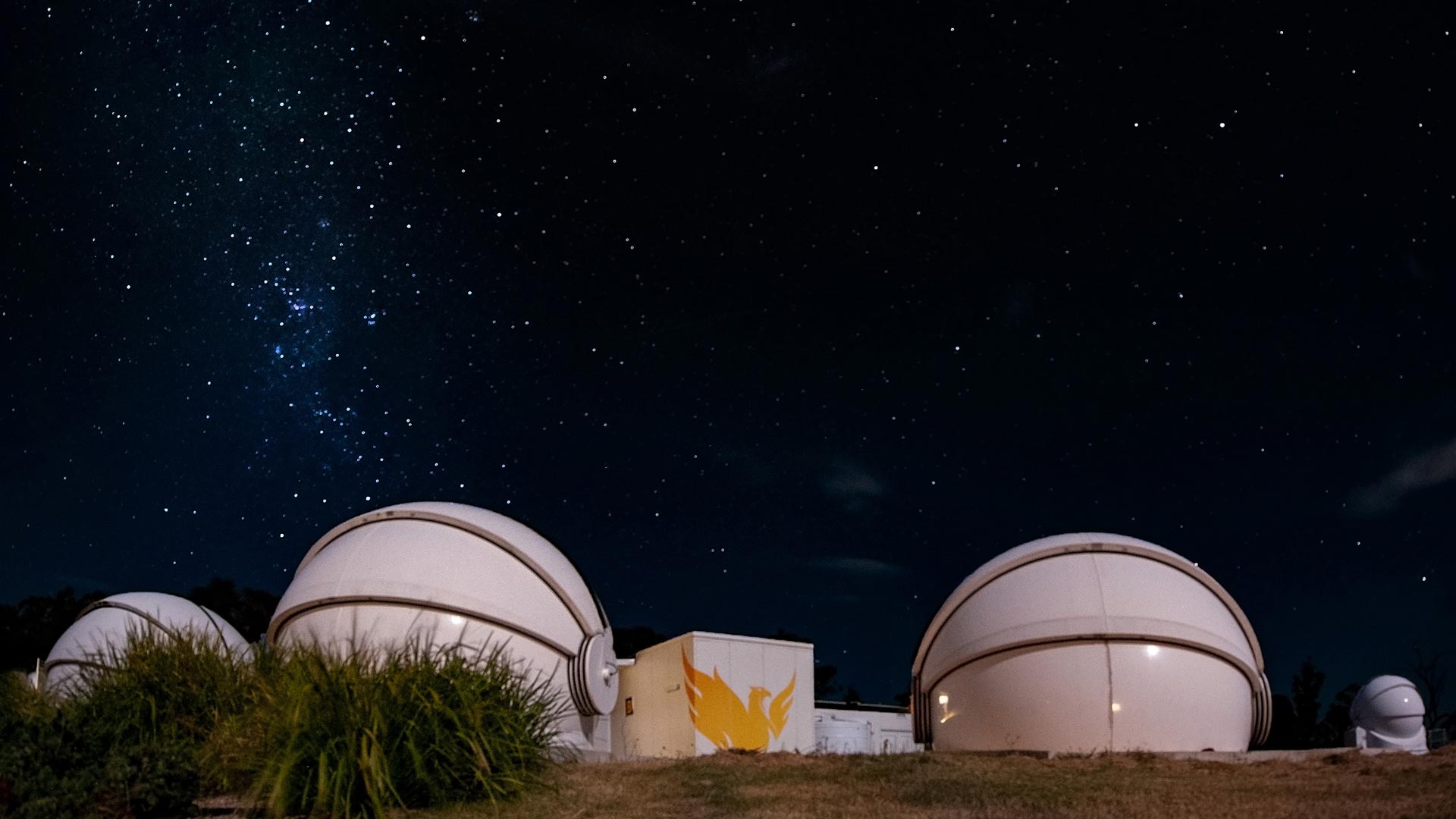 Image Courtesy of UniSQ
Image Courtesy of UniSQMost ground stations in the global space economy are in the Northern Hemisphere. Increasing capacity in Australia will provide more access to time-based services for Australian and other Southern Hemisphere businesses.
Ground stations have specific requirements to operate. They require large areas free from radio traffic, clear skies, dry weather, internet connectivity and security, requirements that Queensland is uniquely positioned to provide.
Our ground systems opportunity
With clear skies and in proximity to the equator, Queensland – particularly Western Queensland – offers multiple locations for ground stations that can scan both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
The ability to purchase satellite data in real time enables new services to grow. For example, real time data can improve decision making for environmental management and disaster relief. Queensland’s space industry and the wider economy could benefit from ground station capability, particularly in:
- the ground system sub-sector – with the opportunity to attract large companies to Queensland
- the space-enabled services sub-sector
- space industry consumers such as the mining, environmental management and agriculture industry sectors
- exports – by enabling the rapid export of data and analytics from Australia to the world through the Sunshine Coast International Broadband Submarine Cable
-
From satellite communications and satellite navigation to Earth observation and remote sensing, the world is increasingly relying on space-enabled services.
In Queensland, the space-enabled services sub-sector is primarily being driven by Earth observation and satellite navigation.
Satellite communications – the US$168 billion Satcom market is shifting from video to data-centric services.
Satellite navigation – the US$126 billion Satnav market has been driven by government-funded systems, which have opened up civilian and commercial activities around the world.
Earth observation – the US$6 billion Earth observation market has historically been dominated by government services. This is changing as commercial opportunities emerge.
Observing Earth from Queensland
Queensland is a world-leader in the field of Earth observation.
The state’s Earth observation sub-sector is the largest in the country and has created a unique cluster through long-term investment in research.
Earth and marine observation has enormous economic benefits to other industries. The value of Earth and marine observation to Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum economies is estimated at US$372 billion.
With Queensland’s proximity to APEC nations and its role as Australia’s leader in Earth observation, its Earth observation ecosystem is positioned to expand through both domestic and international uptake of its products and services. This growth will complement emerging capabilities in Queensland’s ground system sub-sector through increased availability of data.
Space-enabled supply chain opportunities
Demand for space-enabled services drives demand throughout the rest of the space supply chain such as launch and satellite-building programs. More demand for data means more demand for satellites and the capability to build, launch and control them.
Space-enabled services have the potential to grow Queensland’s economy in two ways:
- direct benefits and efficiency gains to consumer industries – particularly in industries that currently have a low awareness of space-enabled services but an untapped potential for growth
- increased demand in the greater space supply chain – by increasing the demand to manufacture, launch and operate space systems to capture data.
-
Our manufacturing base
Queensland’s vast geographical landscape and remote conditions share parallels with space exploration. Queensland also has a long history in robotics and remote asset management through its mining and advanced manufacturing industries.
 Image courtesy of Boeing Research and Technology Centre
Image courtesy of Boeing Research and Technology CentreQueensland’s manufacturers are innovative, customer-focused and seek ways to address emerging issues. The existing advanced manufacturing base includes:
- additive manufacturing technologies
- advanced forming technologies (medical and aerospace)
- advanced materials
- biomanufacturing
- electronics manufacturing (including aerospace and defence)
- heavy engineering
- high temperature superconducting technologies (energy and defence)
- precision tooling and niche machining (including for aerospace)
- technologically superior microwave systems
- next generation broadband and defence systems.
Opportunities to grow and diversify manufacturing
As Queensland’s space industry grows, opportunities will increase for aerospace, defence and manufacturing to diversify into the space supply chain.
For example, Queensland’s leading research and industry organisations are already identifying ways to support the Australian Space Agency and contribute to NASA’s robotics and automation capabilities.
Supporting documents
Industry highlights
Read more aerospace industry highlights.
Last updated: 29 Nov 2024
